What is infertility?
Infertility is a multifactorial disorder that affects approximately 15 per cent of couples of reproductive age. The causes of infertility are equally attributable to men and women.
It can be defined as the inability to achieve or complete a pregnancy after a period of one year of sexual intercourse without contraception.
What are the causes of fertility problems?
There are multiple causes to explain the origin of infertility and several types of classification can be found in the literature depending on the approach to these causes. Like other multifactorial diseases, environmental factors as well as genetic and/or epigenetic abnormalities and/or variants are involved in its occurrence, which makes it very difficult to determine its cause.
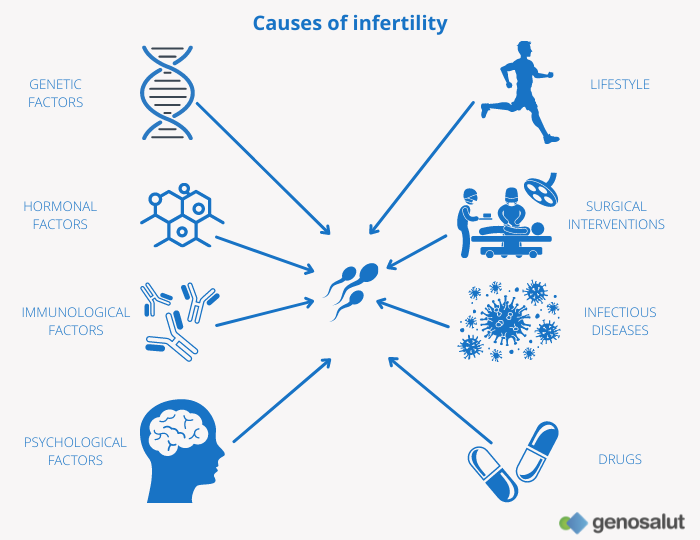
What are the genetic causes of infertility?
In up to 30% of infertility cases the cause may be genetic and affect both men and women.
In couples who are unable to have children, one of the main genetic causes of infertility is chromosomal alterations, whether numerical or structural. In addition to these chromosomal alterations, genetic changes are sometimes detected at the DNA level (mutations in certain genes). In all cases, specific genetic tests may be necessary to identify the cause.
On many occasions, the results of certain genetic tests provide information that allows the cause of infertility to be determined or narrowed down. In this way, the couple can obtain a result that allows them to know their chances of achieving a full-term pregnancy.
Genetic causes of infertility in men
In men, the main genetic causes of infertility are:
● Klinefelter’s syndrome: males with an extra X chromosome (47, XXY). There are also 48, XXXY, and 49,XXXXY cases.
● Microdeletions on the Y chromosome: affecting genes essential for spermatogenesis and proper development of the male gonads.
● Sperm DNA fragmentation: breaks in the genetic material of spermatozoa, which have been associated with reduced fertilisation and pregnancy rates, poor embryo quality and increased rates of miscarriage.
● Frequent mutations: CFTR and AR genes. Mutations in the CFTR gene are responsible for cystic fibrosis, and one of its manifestations is the absence of vas deferens in the testis. Mutations in the AR gene, located on the X chromosome, cause a variety of defects collectively known as androgen insensitivity syndrome.
● Other mutations affecting fertility in men: In recent years, mutations have been detected in several genes that are also associated with certain cases of infertility. These genes include TEX11, AURKC, SYCP3, DNAH1, ZPBP, SYCE1, CATSPER1 and NR5A1.
Genetic causes of infertility in women
In women, the main genetic causes of infertility are:
● Turner syndrome: women who lack one of the two sex chromosomes (XX) in the nucleus of all or part of the cells (mosaic type).
● Mutations in the FMR1 gene: associated with premature ovarian failure.
● Triple X syndrome: cases of premature ovarian failure have been reported in triple X syndrome.
● Mutations in the FSH receptor: may also be associated with premature ovarian failure.
● Thrombophilias
At Genosalut we offer multiple tests to analyse the genetic causes of infertility.
If you like our blog, subscribe to our newsletter


